Dynamic track scales: types and their advantages and disadvantages
Dynamic track scales determine the weight of wagons as they pass over the scales. There are different types, but all of them have electronic sensors built into the track which measure the weight. What all types have in common is that there must be a sufficient approach and departure section in front of and behind the respective scales. All can measure regardless of the direction of travel and whether the train is being pushed or pulled.
In principle, a distinction is made between three different types:
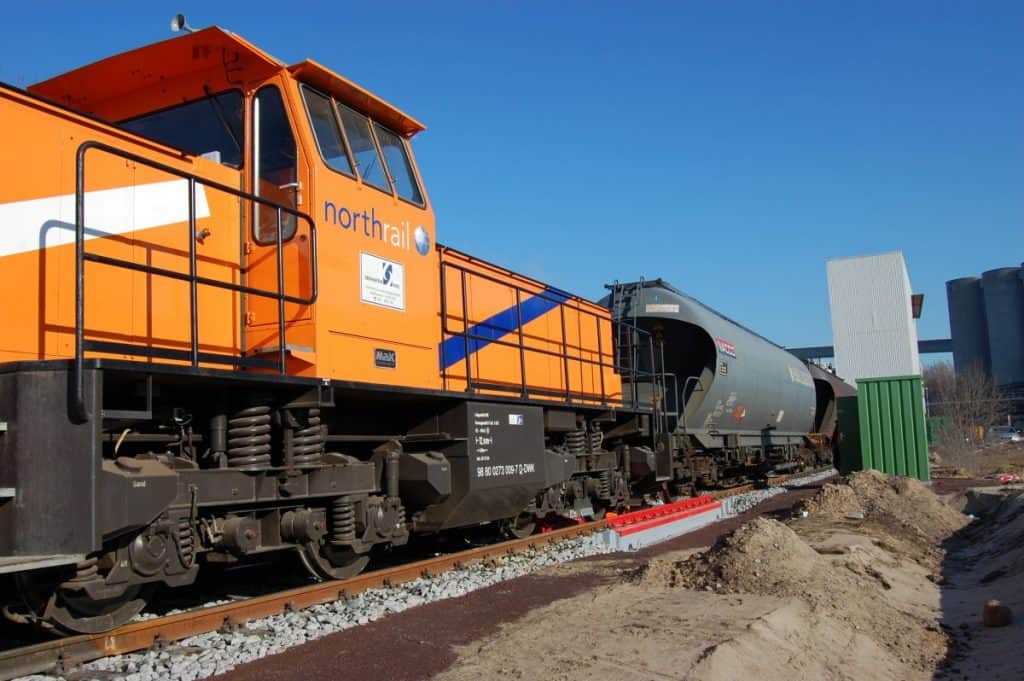
Dynamic track bridge scales
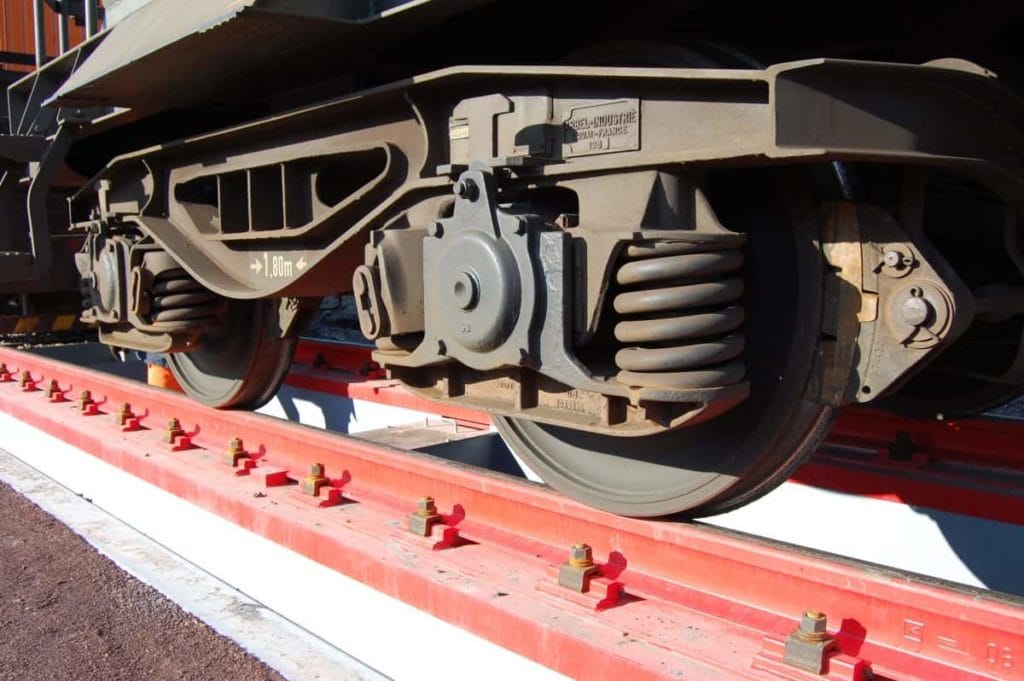
The dynamic weighbridge consists of one or more interconnectable weighbridges. The design of the weighbridge(s) is similar to the static weighbridges with load cells and weighing platform. The rails are mounted on the weighing platform and designed with a rail inclined cut. Rail switches are integrated into the rails to detect the position of the wagons on the scale. Together with the weighing terminal and the software, the weight of the individual wagons or bogies is determined dynamically during the journey at speeds of up to 10 km/h.
Advantages:
- Weighing accuracy class up to 0.2 for individual wagon weights in accordance with calibration regulations and OIML-R 106,
- Thanks to its modular design, liquids can also be weighed dynamically and calibrated,
- Suitable as a static reference scale for calibration, thus saving costs for each recalibration,
- A weighbridge is very robust and durable due to its design like a static rail scale.
Disadvantages:
- No determination of wheel and axle loads, but the design can be extended to include integrated axle load and wheel load measurement with force sensors in the track.

Dynamic track bridge scales
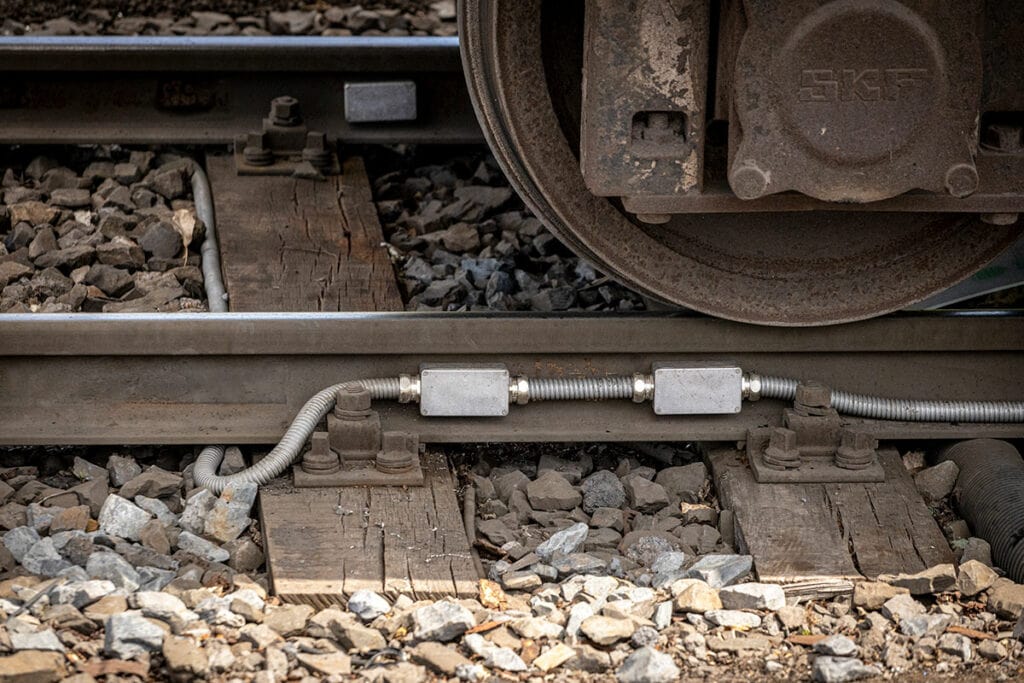
Dynamic track scale with strain gauge in the track
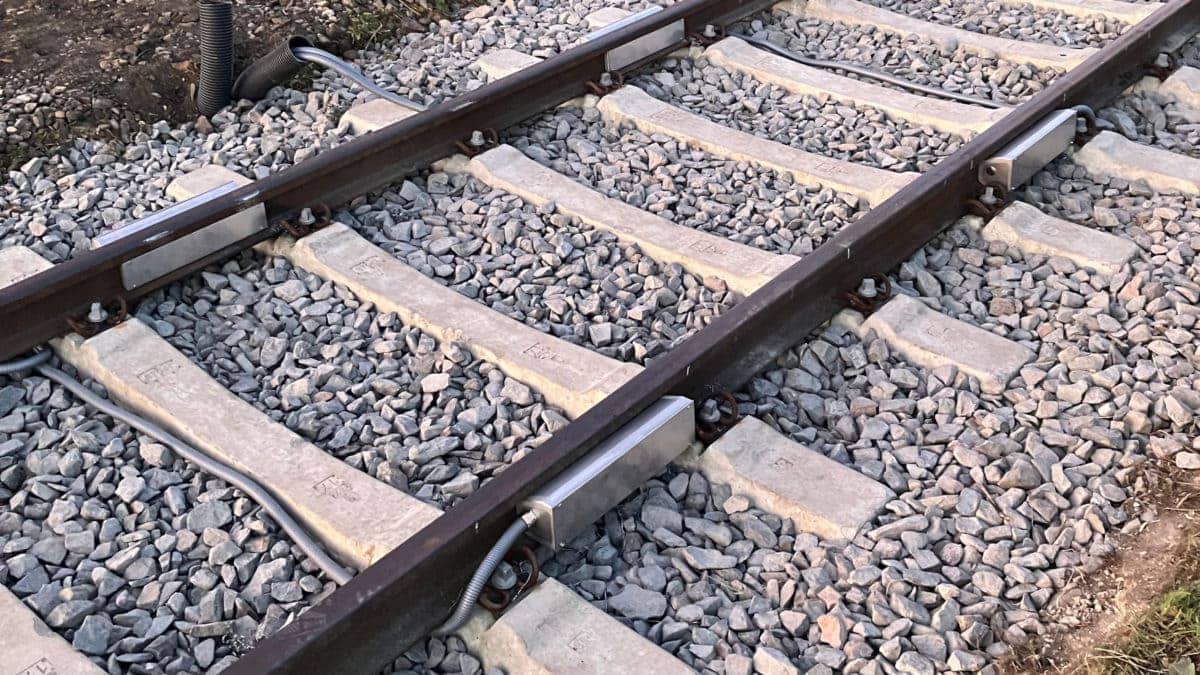
For the dynamic track scale with force sensors, several force sensors are drilled and pressed into the track. If a train runs over the scale at up to 30 km/h, the rail is deformed by the mass of the vehicle (deformation). The change in material tension deforms the sensor, in which strain gauges are fitted in the same way as in a conventional load cell. This allows the weight of the individual wheelset or bogie to be calculated from the specific deformation behavior of the rail.
Advantages:
- Can be used as a wheel load scale and axle load scale,
- Higher measuring speeds possible than with the other two designs,
- Comparatively inexpensive due to the use of only a small amount of hardware and little track construction work.
Disadvantages:
- Not calibratable,
- Accuracy depends on the crossing speed,
- Can only be used for solids.

Dynamic track scale with strain gauge in the track
Dynamic track scales on weighing sleepers
Like the DMS in rail scales, a dynamic track scale based on weighing sleepers is a gapless construction without rail cuts. In simple terms, several sleepers are removed from the track and replaced by weighing sleepers. Load cells are installed in these sleepers. In comparison with the weighbridge, the gapless (and therefore force-coupled) design means that the scales cannot be adjusted statically, but can only work purely dynamically. This requires a very stable substructure without stiffness jumps. The difference to scales with strain gages in the rail is that calibratable sensors can be used for this variant and the scales are therefore calibratable.
Advantages:
- Weighing accuracy class up to 0.2 for individual wagon weights in accordance with calibration regulations and OIML-R 106,
- Like the scale with strain gage in the rail, the hardware scope is small,
- Modular design also enables calibratable dynamic weighing of liquids.
Disadvantages:
- Static reference scale required for dynamic calibration, which increases the cost of recalibration,
- Complex substructure/track construction work required (to ensure long-term stability, resin-based ballast bonding is usually used for the weighing track. This is a process that creates an almost slab track).